Introduction: Toenail removal surgery, also known as onychectomy or toenail avulsion, is a medical procedure that involves the partial or complete. This surgical intervention is typically performed to alleviate severe pain, treat chronic infections, and address underlying conditions that affect the toenail. While toenail removal surgery is generally considered a last resort, there are various circumstances in which it becomes necessary to promote healing, relieve discomfort, and prevent further complications.
Ingrown toenails
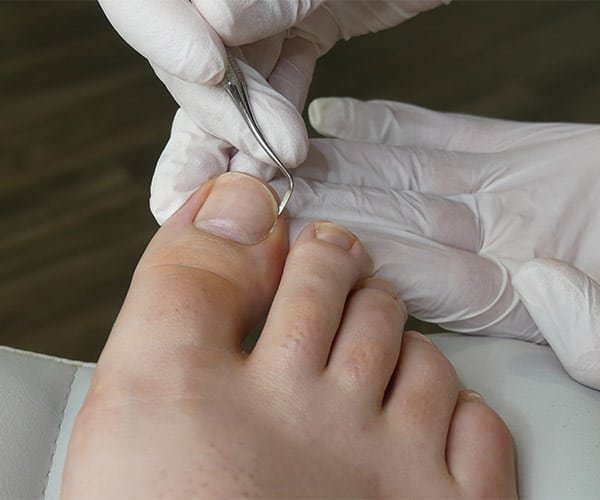
One of the most common reasons for toenail removal surgery is an ingrown toenail. An ingrown toenail occurs when the edge of the nail grows into the surrounding skin, causing pain, swelling, redness, and potential infection. Conservative treatments such as warm soaks and proper nail care are usually attempted first, but if the condition persists or becomes chronic may be recommended to resolve the issue definitively.
Recurrent infections
When a toenail repeatedly becomes infected, leading to persistent pain, pus formation, and difficulty walking, surgical removal may be necessary. Chronic infections can occur due to various factors such as fungal infections, bacterial infections, or complications from an ingrown toenail. By removing the affected nail and addressing the underlying infection, toenail removal surgery can provide long-term relief and prevent the infection from spreading further.
Nail deformities
Certain conditions can cause significant deformities in the toenail, making it difficult to maintain proper foot hygiene or causing discomfort when walking. For instance, nail dystrophy, a condition characterized by thickening, splitting, or crumbling of the nail, may necessitate toenail removal surgery to improve foot function, prevent pain, and minimize the risk of recurrent infections.
Traumatic injuries
Severe injuries to the toenail, such as crushing, avulsion, or severe fractures, may require surgical removal. These injuries can lead to extensive damage to the nail bed and surrounding tissues, making it difficult for the nail to heal properly. In such cases, toenail removal surgery may be performed to promote healing, prevent complications, and facilitate the growth of a new, healthy nail.
Nail tumors or lesions
Although rare, the development of tumors or lesions underneath the toenail can necessitate surgical intervention. Biopsy or complete removal of the affected nail may be required to diagnose and treat potentially cancerous growths, benign tumors, or other abnormal conditions. Early detection and treatment through toenail removal surgery can significantly improve the prognosis and prevent further complications.
While rare, the development of tumors or lesions underneath the toenail can necessitate surgical intervention. To diagnose and treat potentially cancerous growths, benign tumors, or other abnormal conditions, a biopsy or complete removal of the affected nail may be required. Toenail removal surgery in these cases allows for early detection, treatment, and improved prognosis, minimizing the risk of further complications.
Conclusion: Toenail removal surgery is a medical procedure that is reserved for cases where conservative treatments have failed or when there is a significant risk of complications. Whether it’s due to chronic infections, ingrown toenails, nail deformities, traumatic injuries, or the presence of tumors or lesions, this surgical intervention aims to alleviate pain, promote healing, and prevent further damage. If you are experiencing persistent problems, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.

Leave a Reply